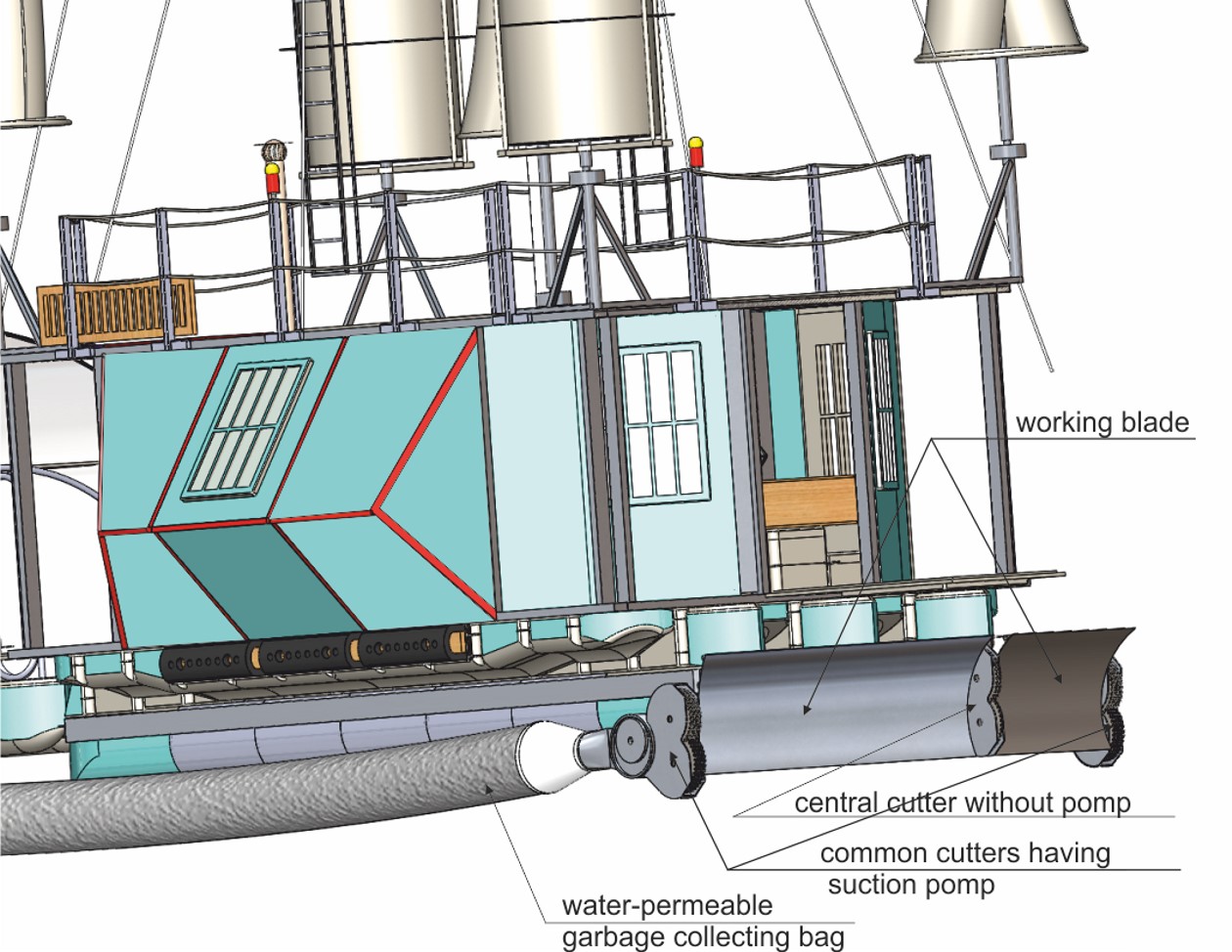
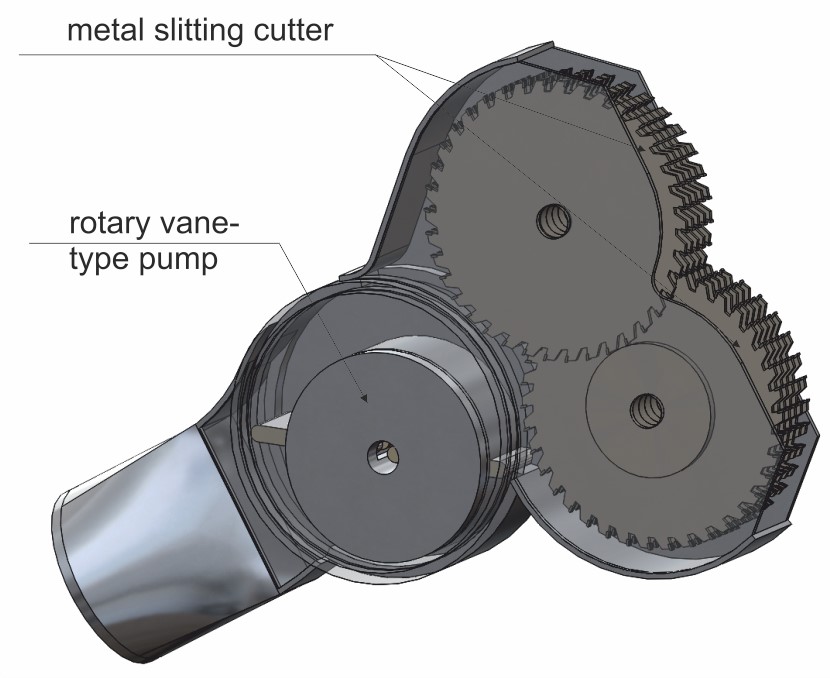
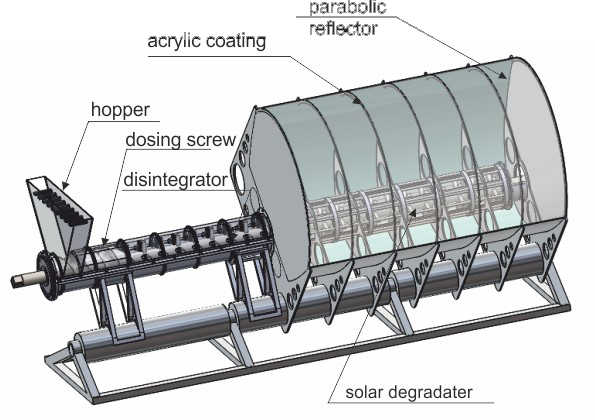
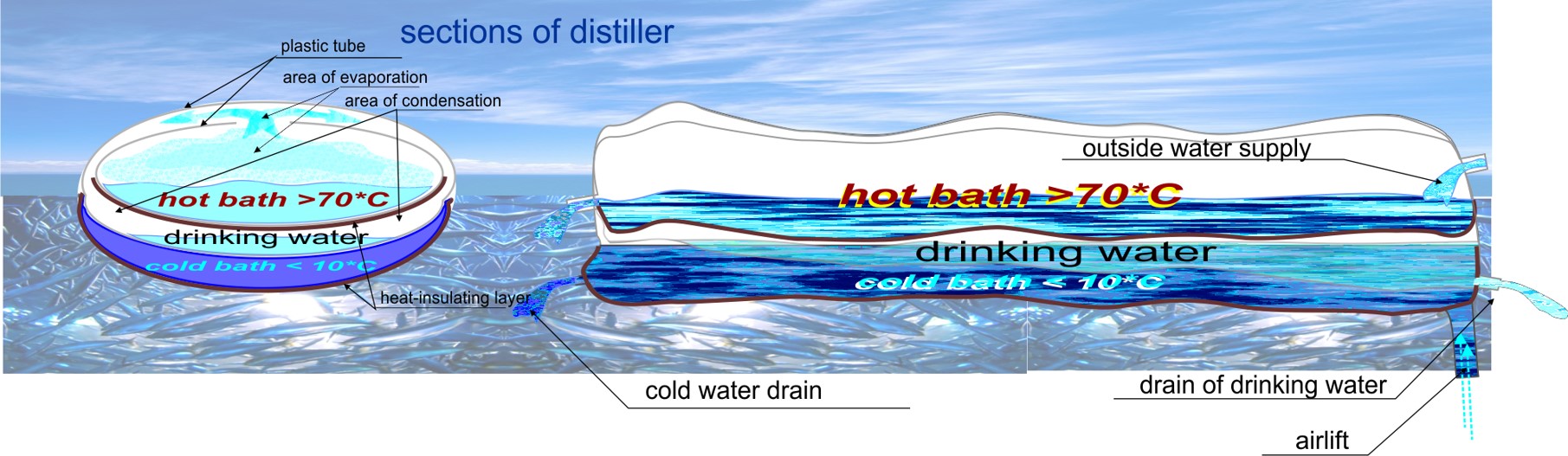
Аннотация:
What were the main mistakes of previous projects!? They did not consider the opportunities that gave the peculiarities of the Sargasso Sea and place of collection of garbage was far away from place of its utilization. Moreover, all the proposed projects were not only subsidized, with a high level of expenditure, but also provided for the removal and storage of garbage in countries adjacent to the Caribbean region. Considering that all of these are developing countries and they do not have a sufficient technological structure to dispose of such an amount of environmentally hazardous waste, this, in essence, was a continuation of colonial policy.
|